
The Story Behind Brahms’s A German Requiem
Johannes Brahms’ Ein deutsches Requiem (A German Requiem), Op. 45, stands as one of the most profound and spiritual works in the choral repertoire. Composed[…]
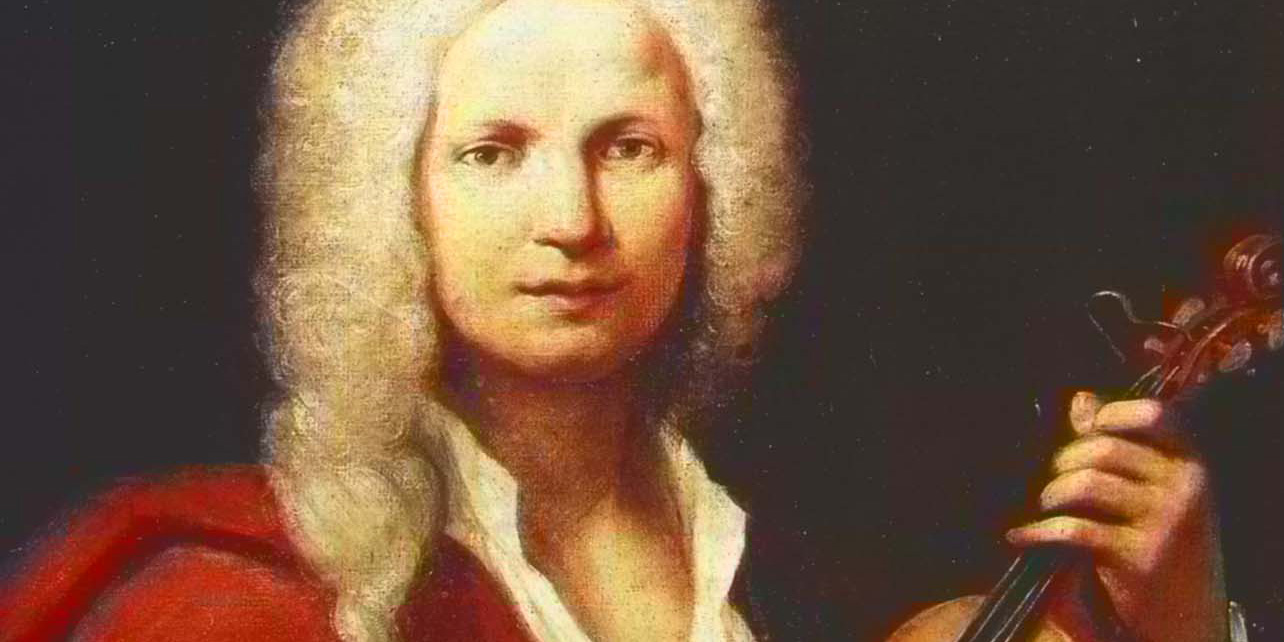

The Story Behind Vivaldi’s Gloria
Antonio Vivaldi, one of the most celebrated composers of the Baroque era, is renowned for his contributions to both sacred and secular music. Among his[…]
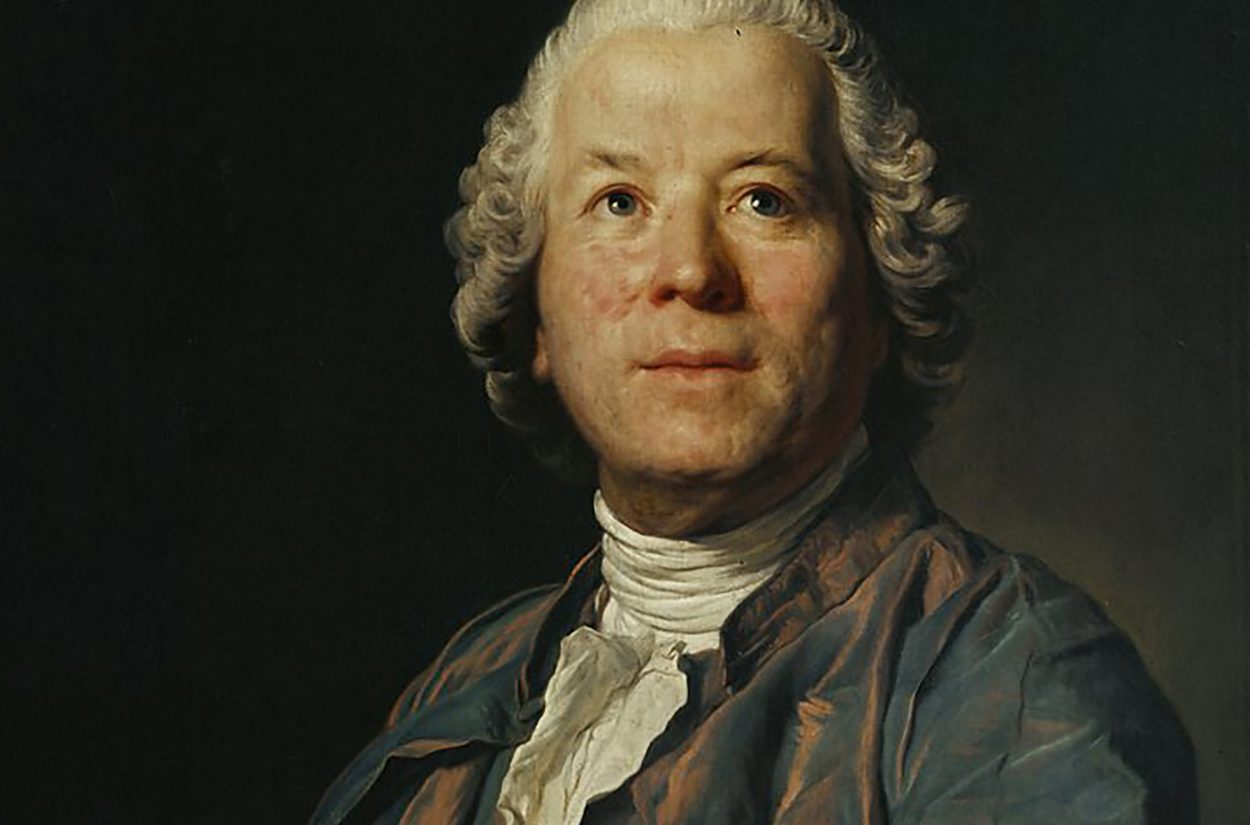

The 5 Best Compositions by Christoph Willibald Gluck
Christoph Willibald Gluck (1714–1787) is celebrated as a transformative composer who redefined opera in the Classical period, bridging the gap between Baroque traditions and more[…]

The 5 Best Compositions by Charles Widor
Charles-Marie Widor (1844–1937) is best known as a towering figure in French organ music. His contributions to organ composition helped shape the instrument’s role in[…]

Top 10 Baldassare Galuppi Songs
Baldassare Galuppi (1706–1785) was an Italian composer and a pivotal figure in the development of opera buffa, the comic opera genre that became immensely popular[…]
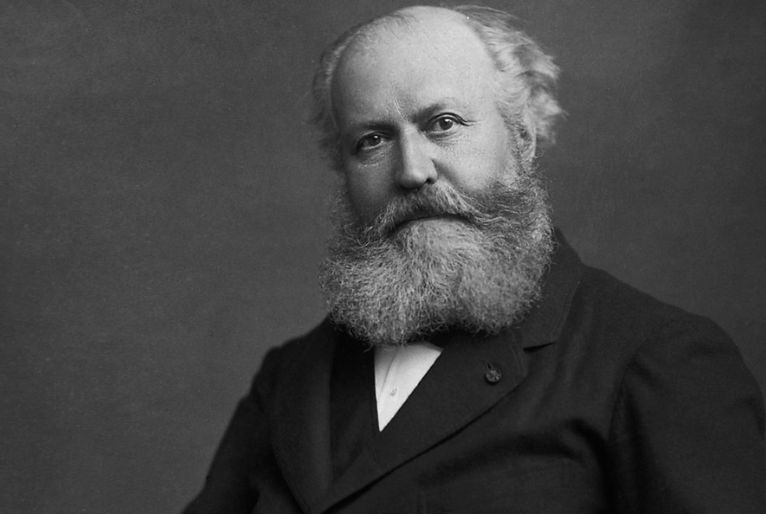
Charles Gounod – Biography and Life
Charles-François Gounod, the celebrated French composer, was born on June 17, 1818, in Paris, France. His life’s melody wove through the Romantic era, leaving an[…]
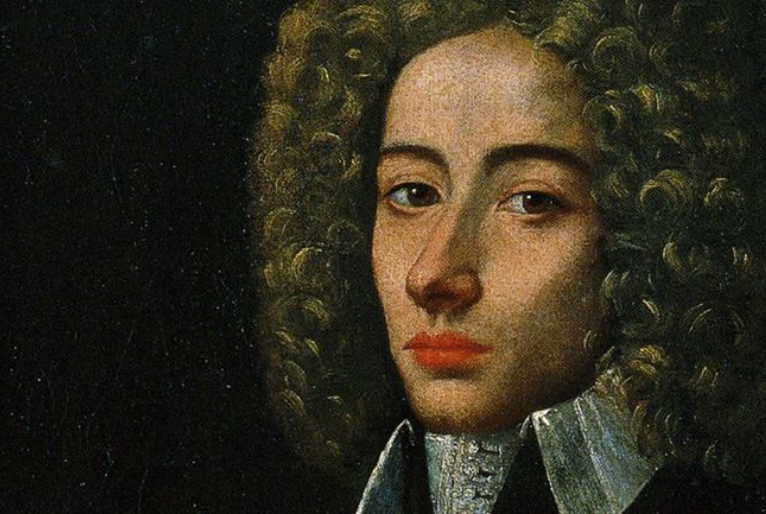

Giovanni Pergolesi – Biography and Life
Giovanni Battista Pergolesi, one of the most renowned composers of the Baroque era, was born on January 4, 1710, in Jesi, Italy. Despite his short[…]

Baldassare Galuppi – Biography and Life
Baldassare Galuppi, often referred to as the “Father of the comic opera,” was a prominent Italian composer of the 18th century. Born on October 18,[…]

Adolphe Adam – Biography and Life
Adolphe Adam (1803–1856) was a French composer and music critic best known for his contributions to the world of ballet and opera. Born on July[…]